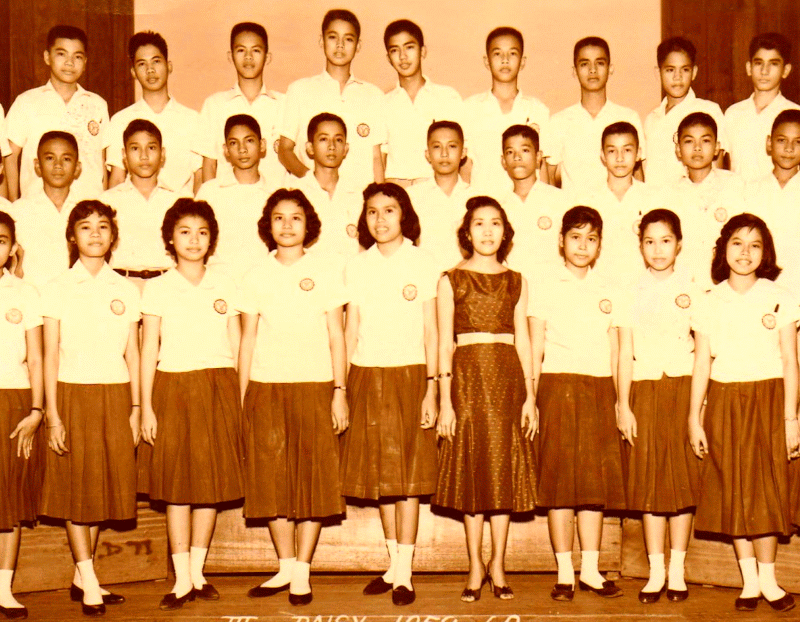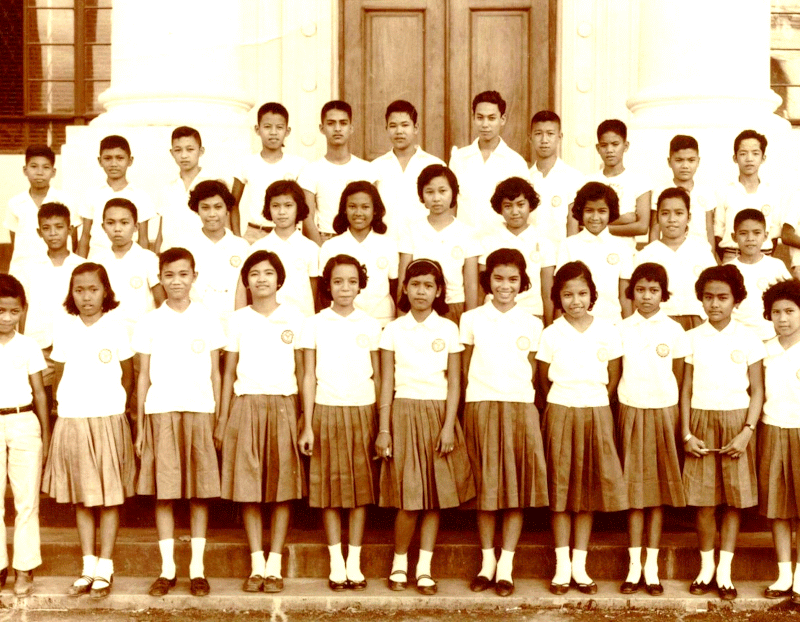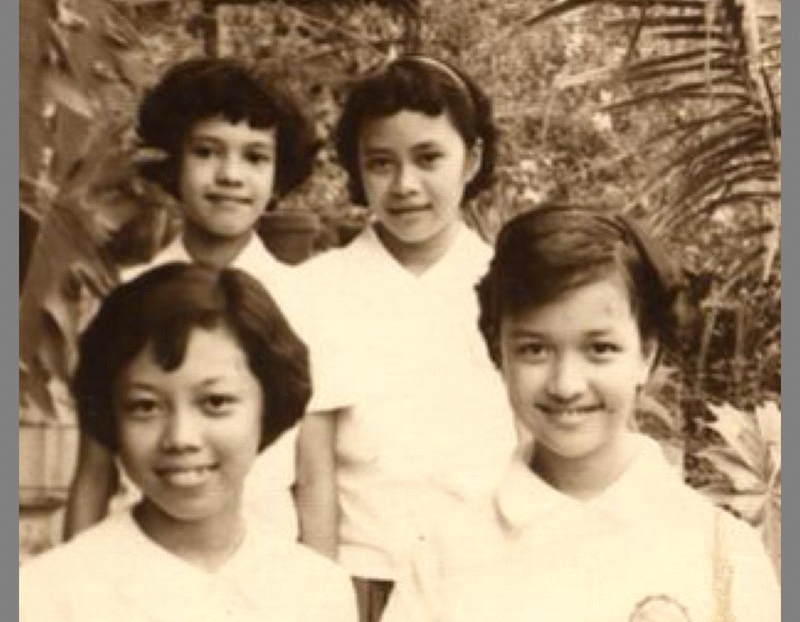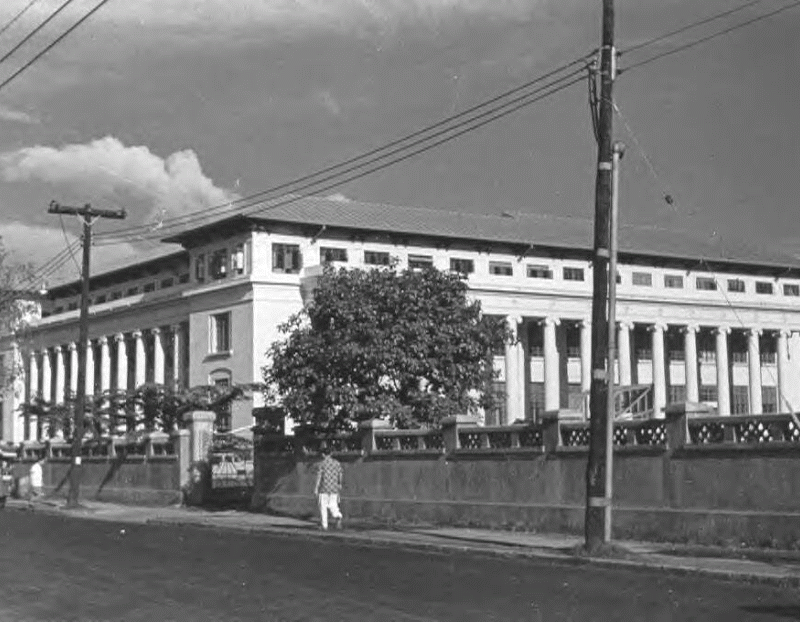
Rizal Hall, University of the Philippines


Independent Philippines and the Third Republic (1946-1972). In April 1946, elections were held. Despite the fact that the Democratic Alliance won the election, they were not allowed to take their seats under the pretext that force had been used to manipulate the elections. The United States withdrew its sovereignty over the Philippines on July 4, 1946, as scheduled.
Manuel Roxas (Liberal Party), having been inaugurated as President as scheduled, on July 4, 1946 before the granting of independence, strengthened political and economic ties with the United States in the controversial Philippine-US Trade Act, In Mar., 1947, the Philippines and the United States signed a military assistance pact (since renewed) which allowed the US to participate equally in the exploitation of the country's natural resources—and rented sites for 23 military bases to the US for 99 years (a later agreement reduced the period to 25 years beginning 1967). These bases would later be used to launch operations in the areas of Korea, China, Vietnam, and Indonesia.
During the Roxas administration, a general amnesty was granted for those who had worked together with the Japanese while at the same time the Huks were declared illegal. His administration ended prematurely when he died of heart attack April 15, 1948 while at the US Air Force Base in Pampanga.
Vice President Elpidio Quirino (Liberal Party, henceforth referred to as LP) was sworn in as President after the death of Roxas in April 1948. He ran for election in November 1949 against Jose P. Laurel (Nacionalista Party, henceforth referred to as NP) and won his own four-year term.
During this time, the CIA under the leadership of Lt. Col. Edward G. Lansdale was engaged in paramilitary and psychological warfare operations with the goal to hold back the Huk Movement. Among the measures which were undertaken were psyops-campaigns which demoralized the superstition of many Filipinos and acts of violence by government soldiers which were disguised as Huks. By 1950, the U.S. had provided the Philippine military with supplies and equipment worth $200 million dollars.
The huge task of reconstructing the war-torn country was complicated by the activities in central Luzon of the Communist-dominated Hukbalahap guerrillas (Huks), who resorted to terror and violence in their efforts to attain land reform and gain political power. They were finally brought under control (1954) after a dynamic attack introduced by the minister of national defense, Ramón Magsaysay. By that time Magsaysay was president of the country, having defeated Quirino in Nov., 1953. His campaign was massively supported by the CIA, both financially and through practical help in discrediting his political enemies. He had promised sweeping economic changes, and he did make progress in land reform, opening new settlements outside crowded Luzon Island. His death in an airplane crash in Mar., 1957, was a serious blow to national morale. Vice President Carlos P. García succeeded him and won a full term as president in the elections of Nov., 1957.
In foreign affairs, the Philippines preserved a firm anti-Communist policy and joined the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization in 1954. There were difficulties with the United States over American military installations in the islands, and, in spite of formal recognition (1956) of full Philippine sovereignty over these bases, tensions increased until some of the bases were dismantled (1959) and the 99-year lease period was reduced. The United States rejected Philippine financial claims and projected trade revisions.
Philippine opposition to García on issues of government corruption and anti-Americanism led, in June, 1959, to the union of the Liberal and Progressive parties, led by Vice President Diosdado Macapagal, the Liberal party leader, who succeeded García as president in the 1961 elections. Macapagal’s administration was marked by efforts to combat the mounting rise that had plagued the republic since its birth; by attempted alliances with neighboring countries; and by a territorial argument with Britain over North Borneo (later Sabah), which Macapagal claimed had been leased and not sold to the British North Borneo Company in 1878.
Inside the walls of Intramuros, The location of MIT.One of the seven Gates. The construction of Intramuros started in 1571 by Miguel Lopez de Legaspi, a Spaniard. The walled city covers an area of about 160 acres. Intramuros was a fortress city with walls 6 metres high and a commanding 3 kilometres in length, it is no wonder it was impenetrable. Only the Spanish elite and Mestizos (mixed race) were permitted to live inside Intramuros, where at night the city gates were locked down.

intramuros, manila cathedral
The natives and Chinese were not permitted to live inside the walled fortress and were resigned to live outside the great walls of Intramuros. Intramuros was designed with 51 blocks within the vast walls, the only access in or out of Intramuros was via seven fortified gates. A moat around the walled city was added in 1603. Spread throughout the 51 blocks of the city were 12 churches, hospitals, domestic accommodation, military barracks, Governors Palace and schools.

My Church in the town of my birth:Tanay, Built in 1778, the church was named after the Archbishop Ildefonso of Toledo, Spain, who was consecrated during the year 657 AD; revered for his spiritual vitality and deep writings contained in “ The Book of the Virginity of Maria”. Behind the heavy stone edifice decorated with Hispanic, archetype windows and stone sculpture of its saint, are legends that found its way to this generation. Tradition has it that an image of the Lady of the Immaculate Conception, was found among the belongings of our fleeing forefathers on the onset of the Spanish Invasion in 1573; the same image found among the remnants from the fire that gutted the first church in 1620- a lone survivor! During the Chinese Uprising in 1639, Father Geronimo de Frias hid it in the fields but was later on found by the Chinese rebel who tried to destroy the image, instead to themselves befell violent death.
Cross at Bukal, in Tanay
This was always sang to me by my grandmother. Presented in this video are the vintage photographs of the following colonial and historical religious edifices:
1. La Loma Church - formerly Caloocan, now Manila
2. Sto Domingo Church- Intramuros (destroyed by the Americans during world war II)
3. Paco Catholic Cemetery - Paco
4. Tondo Church -Tondo
5. San Sebastian Church -Manila
6. Binondo Church - Binondo
7. San Juan Church - San Juan
8. Sta. Cruz Church - Manila
9. Manila Cathedral - Intramuros
10. Poong Nazareno Church - Quiapo
Television was introduced in the Philippines in 1953 with the opening of DZAQ-TV Channel 3 of Alto Broadcasting System in Manila. The station was owned by Antonio Quirino, the brother of the incumbent Philippine president, who was set to run for re-election the following year. The station operated on a four hour-a-day schedule (6 - 10 p.m.) and telecast only over a 50-mile radius. This television station was later bought by the Chronicle Broadcasting Network which started operating radio stations in 1956. CBN was owned by the Lopezes who were into various business concerns. The acquisition signalled the birth of ABS-CBN Broadcasting Network, now considered one of the major broadcasting companies not only in the Philippines but also in Asia. The Lopezes also owned The Manila Chronicle, a leading daily at that time. ABS-CBN therefore became not only the first radio-TV network in the Philippines but also the first cross-media entity owned by a family --- a situation which remains until today. Subsequently, the Lopez group added a second station, DZXL-TV 9. By 1960, a third station was in operation, DZBB-TV Channel 7 or Republic Broadcasting System, owned by Bob Stewart, a long-time American resident in the Philippines , who also started with radio in 1950. The first provincial television stations were established in 1968 in Cebu, Bacolod, and Dagupan by ABS-CBN. The network is supplemented by 20 radio stations located nationwide.
Economic constraints during these early years of television forced a dependence on imported programs from three U.S. networks – ABC, CBS, and NBC. Importing programs was cheaper than producing them locally. In addition, canned programs appeared to be more popular among local audiences, even though initiatives were made in educational programming.
The commercial thrust of Philippine broadcasting has made it unique among other East Asian countries, where the electronic media are controlled and operated by the government. While this free enterprise environment made local broadcasting globally competitive, the same environment made it difficult to produce and broadcast public service and "development" oriented programs.
Philippine television's early dependence on US programs may be partly responsible for "colonial mentality" that has continued to afflict Filipinos during the past several generations. The commercial orientation of TV also engendered a "that’s entertainment" mentality in both the advertisers and the general public.
|

Supreme Court Building C/ Padre Faura
Ermita, Manila, next above photo was class ‘61 UP Prep
Building at the right is Rizal Hall, the location of my University of the Philippines Prep High School.
Photo of Rizal Hall below was taken in 1950. | | |
Early 1960:I remember the old beautiful architectural lines of the Manila Hotel, not the new monstrous addition as it is now. it reinforces the fact that much of the loss of the quality of life in the metropolis owes to crass commercialism, slapdash development, and the regulated chaos that makes up for urban planning in the otherwise overly regulated and bureaucratized regime in the Philippines. I reflect the times in High School when we trek on to this site from Padre Faura, Rizal Hall to the US Embassy Canteen to buy our ice cream cone for 10 centavos. Pleasant memories too of my first exposure to teen age westerners on one to one basis in this Hotel at pool side parties. This song jogs the memory lane.

US Embassy Compound, near Rizal Park, Manila, as seen from the Filipinas Hotel. Port of Manila in background. I reflect the times in High School when we trek on to this site from Padre Faura, Rizal Hall to the US Embassy Canteen to buy our ice cream cone for 10 centavos.
| | |
 | |
US Embassy Manila
|

Tanay, Rizal
|

 Wack Wack Golf & Country Club is one of the oldest golf clubs in the Philippines, having been founded in 1930 by a prominent American resident William J. Shaw. Established as an exclusive championship course in the then town of Mandaluyong (now Mandaluyong City) in the metropolitan area of Manila, it has consistently been considered as one of the best golf courses in world. It was the home of the Philippine Golf Open Championships, the traditional kick-off site of the annual Asian Circuit, and site of numerous world golf events like the World Cup and others. Wack Wack Golf & Country Club is one of the oldest golf clubs in the Philippines, having been founded in 1930 by a prominent American resident William J. Shaw. Established as an exclusive championship course in the then town of Mandaluyong (now Mandaluyong City) in the metropolitan area of Manila, it has consistently been considered as one of the best golf courses in world. It was the home of the Philippine Golf Open Championships, the traditional kick-off site of the annual Asian Circuit, and site of numerous world golf events like the World Cup and others.
|
|
|
| |

|
Below photo of Sarmiento building on Ayala Ave. Then after, is Roxas Boulevard at twilight. Beyond is the breakwater protecting the harbor basin of the Navy and the Manila Yacht Club. This was the seaside Avenue at the MNS where we lived, the attraction was the sunset across Manila Bay which I took for granted. This truly beautiful sight served a fitting backdrop for the many hundreds of families and lovers who still flock there each evening to enjoy the cool breeze and precious moments together. The garish artificial illuminations of Luneta take over at dusk, but it surely pale in comparison to the grandeur of the setting sun, nature’s own design for Roxas Boulevard, as the sun slowly descends behind the Bataan peninsula.
|
|
|